Foods to avoid when diagnosed with hyperkalemia

Hyperkalemia is a health condition when the blood has a high potassium level. Potassium in your blood handles functioning muscle, nerve cells and maintains fluid balance. In normal conditions, the blood potassium level is 3.6 to 5.2 mill moles per liter (mmol/L). If the potassium level is 6.0 mmol/L or above, it can be potentially harmful for the body and needs immediate treatment.
To treat hyperkalemia, your doctor will provide you with treatment options and might also recommend a low-potassium meal plan. Changes in meal routine can help you maintain the blood potassium level. However, some food items can raise these levels, leaving you to avoid them.
A low potassium meal plan is the main solution to control hyperkalemia. However, that does not mean you have to avoid high-potassium foods. You may eat foods that react with your body and raise your potassium level. Moreover, you must avoid potassium intake and limit it to 2000 milligrams per day. Your doctor can help you plan a food regime to maintain potassium levels.
You can find potassium in food items like fruits, dairy, snacks, vegetables, and drinks. You cannot completely avoid them. That is why you need to avoid or limit some food items as mentioned below.
Fruits and vegetables
Doctors always advise fruits and vegetables for good health. However, if you are suffering from hyperkalemia, you can avoid a few. You should limit the intake of a few foods. You should avoid fruits like apricots, avocados, kiwis, mangoes, and oranges. Not all fruits are bad for your health, but consider these for a proper routine. In addition, one must avoid beetroot, spinach, pumpkin, tomatoes, and mushrooms.
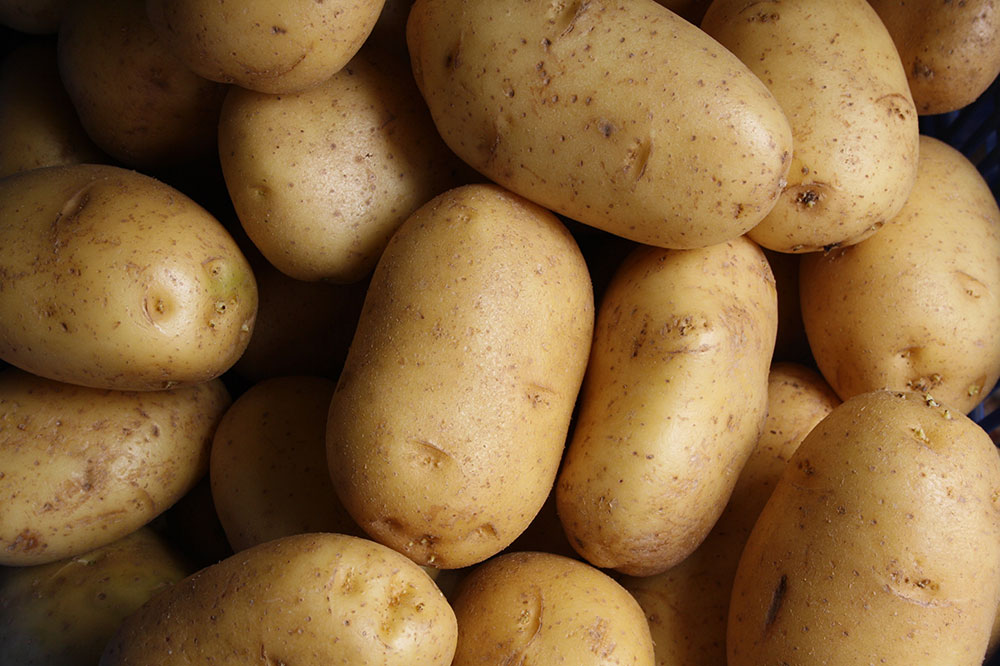
Baked potato
A baked potato has 950 milligrams of potassium. Even if you want to consume baked potatoes, try peeling off the skin, as 60% of potato skin has potassium. Also, try to boil the potatoes for a few minutes and drain the water. This way, you can remove the potassium.
Cooked lentils
Cooked lentils can add up to 700 milligrams of potassium to your food cycle. Other legumes, like soybeans and kidney beans, are also considered high in potassium. They contribute around 300 to 500 milligrams.
Tomato products
With almost 650 to 670 milligrams, tomato paste contains a rich amount of potassium. A half-bowl of tomato paste has 550 milligrams. A medium-size tomato stores over 250 milligrams. Therefore, it advised to limit the intake of this vegetable.
Banana
Bananas, as a fruit, store 442 milligrams of potassium. Therefore, you should avoid the fruit as much as possible. Moreover, fruits like apples and oranges have about 5% potassium. A banana is a food item that has its own drawbacks and benefits.
Milk
Milk products are one of the richest sources of potassium. Milk items store 367 milligrams, and yogurt with the same number of calories contains 440 milligrams.
Other potassium-rich foods are also important to avoid. Items such as cereals with dry fruits, salt substitutes, and chicken breast are on the list. You do not need to completely stop taking these foods. However, excessive intake of these food items can trigger potassium levels in the blood. Limit its intake as per the recommended potassium level per day. Moreover, doctors will help you tweak your food schedule according to your health requirements.
You need to manage your food regime with low-potassium food items. One also needs to limit the intake of the above-mentioned foods. It will help you manage hyperkalemia and its symptoms like abdominal pain, nausea, chest pain, muscle weakness, among others.